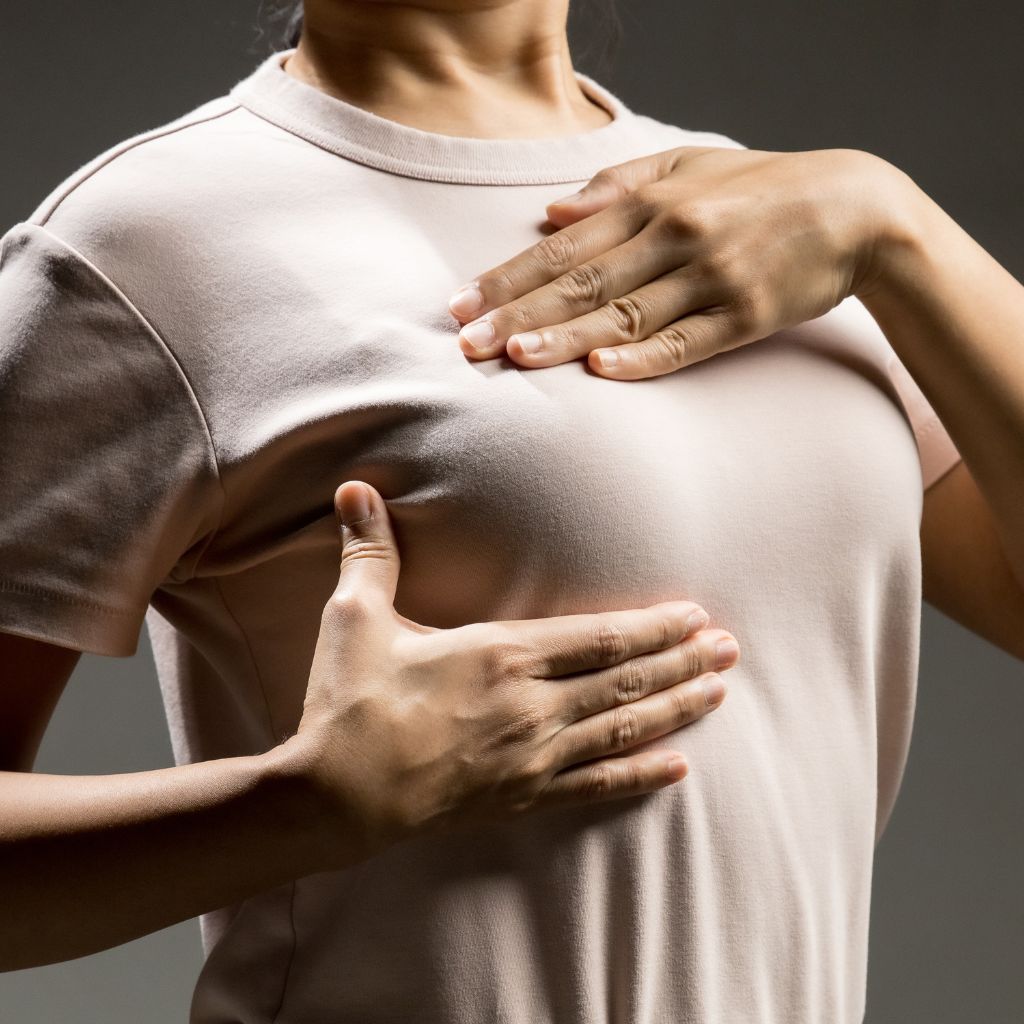
When it comes to being proactive about our health, taking a few moments for the simple task of a breast self-exam can reap serious benefits. In fact, the concept is quite straightforward: A breast self-exam is basically a process of checking your own breasts for any changes indicating possible problems.
It’s important that women actively look out for signs of potential issues because early detection can be key to a successful medical outcome. Now let’s take a quick glance at this intro guide to the basics of performing self-breast exams and what to look out for! Put on some peppy music and let us help you make your way through this mammary mission. Ahoy!
Definition of a breast self-exam
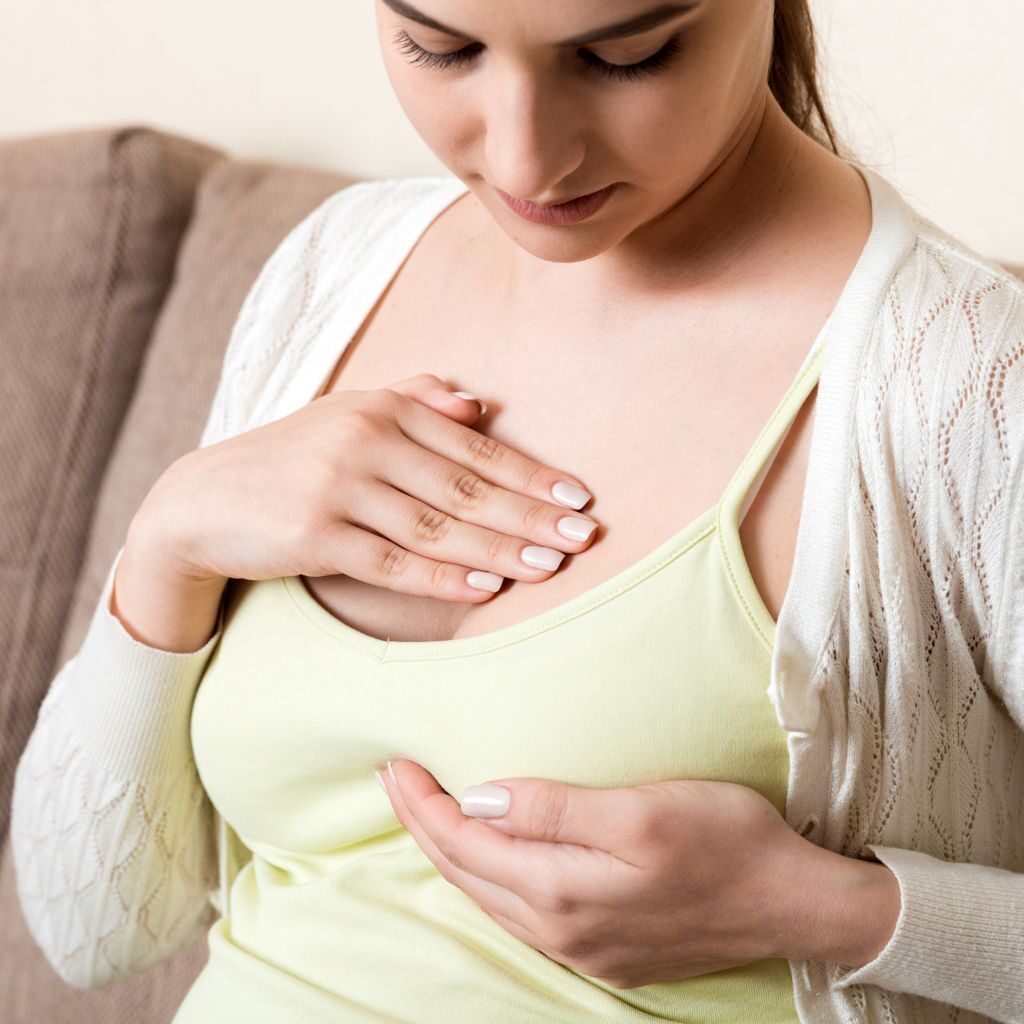

Why performing a breast self-exam is important
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Breast Self-Exam
Taking care of your health is paramount and knowing how to conduct a breast self-examination is an important part of this. A breast self-exam can help you identify abnormalities that may be undetectable in a clinical exam so it’s important to understand the steps involved. To start, preparing for a breast self-exam requires being aware of what to expect and understanding how best to get ready – what techniques and tools to use, etc.
During the examinations, visual cues such as symmetry and any changes in size, shape, or texture are important factors to pay attention to. Additionally, feeling each breast using three different techniques (circling, pressing, and flicking) should also be included in the examination process. Understanding these steps are key in conducting an effective breast self-exam and can help you detect potential issues or tumors sooner rather than later.
Preparing for the Exam: What to Expect and How to Get Ready
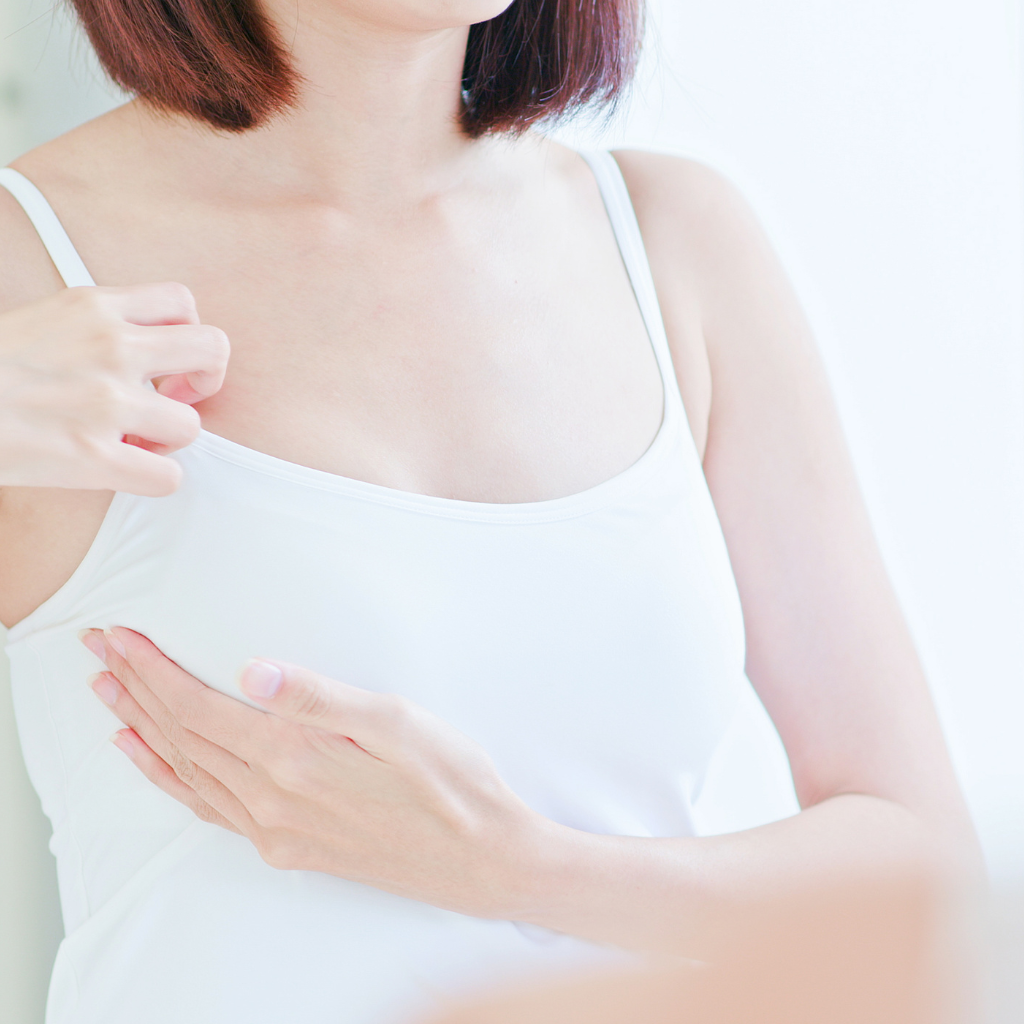

Examining your Breasts: Tips for Identifying Abnormalities and Tumors
When examining your breasts it is important to look at them in the mirror with your arms at your sides and then with them raised above your head. Take special notice of any asymmetry between the two breasts as well as any changes in size, shape, or texture. Also feel each breast using three different techniques (circling, pressing, and flicking) as well as your armpits and around your collarbone for any lumps.
Lastly, it is important to check in with yourself on a weekly or monthly basis to compare any changes you may find during the examination. If something unusual is found it is best to make an appointment with a doctor right away. Taking these steps is vital in order to detect potential issues or tumors sooner rather than later.
While there is no substitute for regular visits with a medical professional, knowing how to perform a breast self-examination can be empowering and help women take charge of their own health. By following the steps outlined above, women can become more familiar with their own bodies and be better equipped to spot any abnormalities that could indicate an issue earlier rather than later. Doing so will help provide peace of mind and potentially save lives.
It should be noted that breast self-exams are not a substitute for regular medical visits and should never replace mammograms or other tests recommended by your doctor. If you have any questions about the breast self-examination process, be sure to consult with your physician.
The importance of early detection can’t be overstated so taking the time to become familiar with your breasts through self-examination is a necessary step in order to detect potential issues or tumors earlier rather than later. Performing regular breast self-exams is an easy and effective way for women to take charge of their own health and ensure they remain healthy for years to come.
The Importance of Early Detection

Early detection is key to successful treatment and survival when it comes to any type of cancer, including breast cancer. According to the World Health Organization, early detection of breast cancer can reduce mortality from the disease by up to 25%. Therefore, it is vital that women become familiar with their own bodies through self-exams and keep an eye out for any changes or abnormalities that could indicate an issue.
Although there is no single test that can detect all types of breast cancer, regular breast self-exams are a crucial tool in detecting potential issues sooner rather than later. Women should make sure they know what normal looks and feels like for them so they can quickly identify any changes that arise.
By being aware of the importance of early detection and taking the steps necessary to monitor their own health, women can be empowered to take charge of their well-being and potentially save their lives.
After Your Exam: What to do if You Find Something Abnormal
It can be an emotional experience to discover something unusual during a self-exam, so don’t hesitate to reach out for emotional support if you need it. Remember that most abnormalities found during self-exams turn out to be benign, so try to stay positive and take charge of your own health.
Early detection is key to successful treatment and survival when it comes to any type of cancer, so taking the time to become familiar with your breasts through self-examination is a necessary step in order to take control of your own well-being.
Conclusion

Although there is no single test that can detect all types of breast cancer, regular breast self-exams are an important tool for detecting potential issues earlier rather than later. By becoming familiar with their own bodies through self-examination, women can better equip themselves to spot any changes or abnormalities that could indicate a medical issue before it becomes too serious. Additionally, doing so will provide peace of mind and potentially save lives by allowing for early detection and treatment of potential issues.
By following the steps outlined in this article, women can be empowered to take charge of their health and ensure they remain healthy for years to come. Early detection is key to successful treatment and survival when it comes to any type of cancer, so taking the time to become familiar with your breasts through self-examination is a necessary step in order to take control of your own well-being.
With these tips in mind, you are now more aware and better equipped to perform regular breast self-exams — an important tool for early detection that could potentially save lives.
Resources
World Health Organization: Early Detection & Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
https://www.who.int/cancer/detection/breastcancer/en/
Mayo Clinic: Breast Self-Exam
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/breast-self-exam/about/pac-20393868
National Breast Cancer Foundation: How to Perform a Breast Self Exam
https://www.nationalbreastcancer.org/breast-self-exam/
Susan G. Komen: How to Do a Breast Self-Exam
https://ww5.komen.org/BreastCancer/HowtoDoaBreastSelfExam.html
National Cancer Institute: Breast Cancer Screening (PDQ®)–Patient Version
https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/breast-screening-pdq
Breastcancer.org: Breast Self-Exam
https://www.breastcancer.org/symptoms/testing/types/self_exam
American Cancer Society: How to Do a Breast Self-Exam (BSE)
https://www.cancer.org/latest-news/how-to-do-a-breast-self-exam.html
American Assurance USA Blog on Health/Women’s Health https://americanassurance.net/blog/
Disclaimer
This article is intended to be informational and educational in nature, but should not replace professional medical advice. Be sure to consult your physician if you have any questions or concerns about performing a breast self-exam.
Do not delay seeking or disregard medical advice based on the information contained herein. The opinions expressed herein are not necessarily those of the author, publisher, or its affiliates.
By taking the time to learn how to perform a proper breast self-exam, all women can ensure they remain healthy for years to come and take control of their own health and well-being by being aware of changes that could indicate potential issues with their breasts. Early detection is key so don’t delay—start performing regular breast self-exams today!
If you have any questions or concerns about performing a breast self-exam, please consult your physician. Do not delay seeking or disregard medical advice based on the information contained herein. The opinions expressed herein are not necessarily those of the author, publisher, or its affiliates.